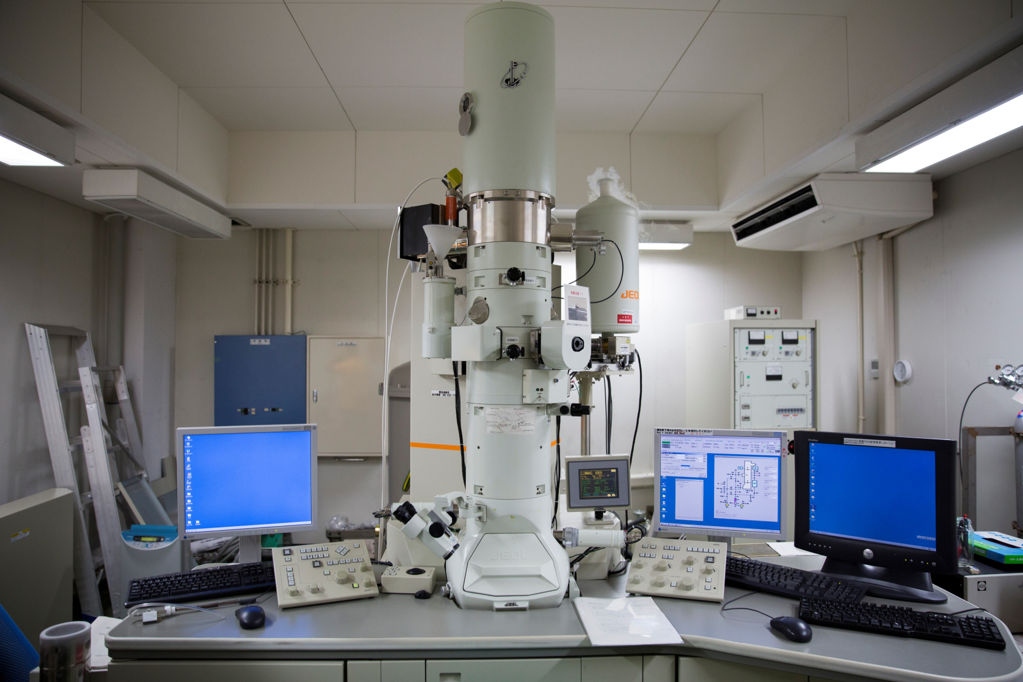
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopic technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The device is used for shape and morphology investigation of the synthesized nanomaterials.

Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning the surface with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that contain information about the surface topography and composition of the sample. The device is used for surface morphology investigation of the synthesized nanomaterials.

X-ray Diffractometer (XRD)
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a technique in which the constructive interference of monochromatic X-rays and a crystalline sample is considered to study crystalline structure of materials. The device is used for investigating the amorphous/crystalline phases of the synthesized nanomaterials.
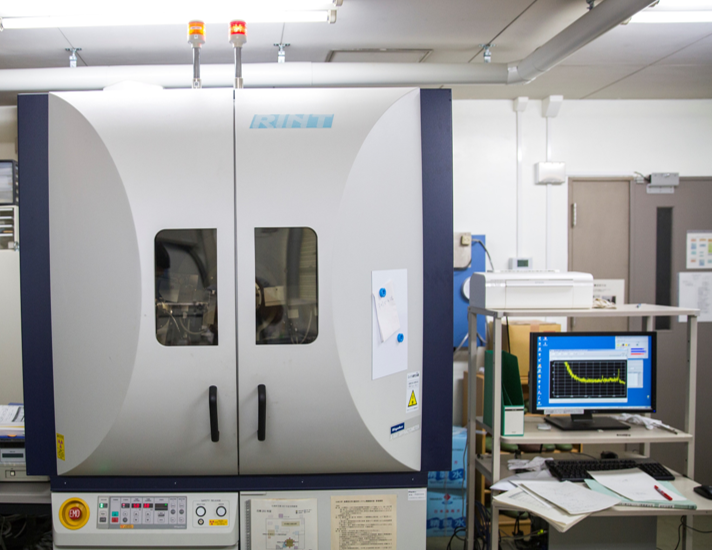

Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a technique used to obtain an infrared spectrum of absorption or emission of a solid, liquid or gas. An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high-resolution spectral data over a wide spectral range. The device is used for the determination of the elemental bonding and functional groups in the synthesized nanomaterials.

BET Surface Analyzer
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area analysis is a technique in which gas (nitrogen) physisorption is used to measure and analyze surface area in porous materials. The gradual increase in gas pressure causes the adhesion of more and more molecules to the surface. The smaller the pores the larger the surface area available for gas adsorption which is measured by carefully monitoring the volume and pressure of the gas at constant temperature. The device is used to determine the surface area and pore size characteristics of the synthesized nanomaterials.

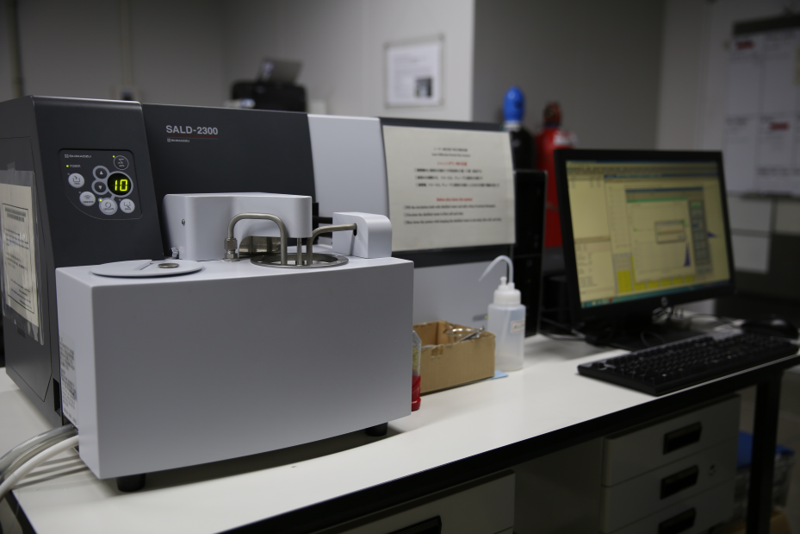
Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyzer (SALD)
Laser diffraction is a technique used for the determination of materials’ particle size based on the measurement of light angle scattered by the particles as they pass through a laser beam. The device is used for the measurements of particle size and size distribution of the synthesized nanomaterials.

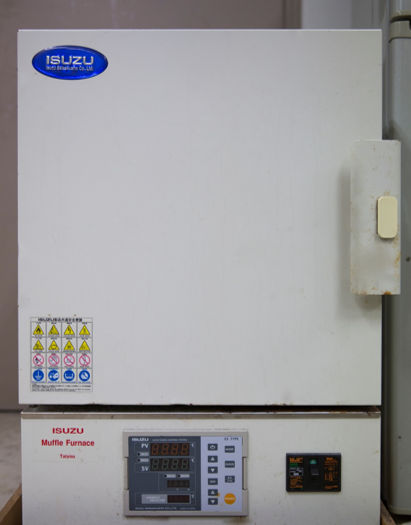
Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace or muffle oven is a furnace in which the subject material is isolated from the fuel and all the products of combustion, including gases and flying ash. The device is used for the calcination and carbonization of the synthesized nanomaterials, and other process which require very high temperature (up to 1400 0C).

Drying Oven
A drying oven introduces fresh dry air to the chamber and expels the warm moist air simultaneously allowing to rapidly dry the samples. The device is used to provide high-performance drying and heating of the samples.

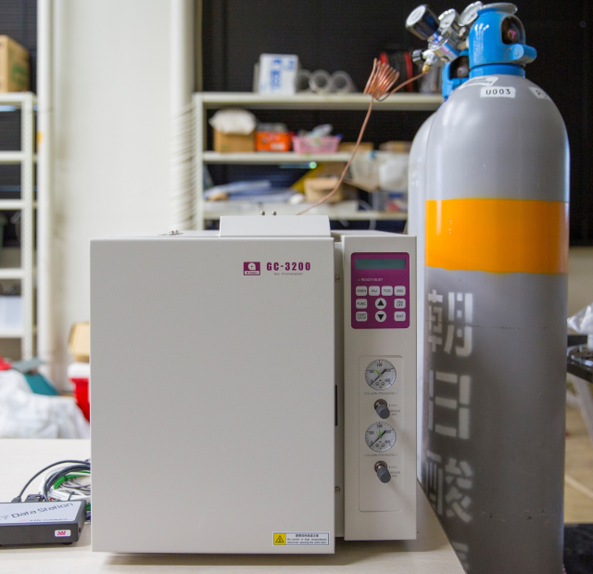
Gas Chromatograph (GC)
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common technique used for separating and analyzing chemical compounds, that can be vaporized without decomposition, in a complex sample. GC device is used for the biogas and methane measurements.

UV-Visible Spectrophotometer (Wavelength range: 320 - 1100 nm)
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometry is a technique used to measure light absorbance across the ultraviolet and visible ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. UV spectrophotometer use this principle to quantify the analytes in a sample based on their absorption characteristics. The device is used for the concentration measurements of several chemical elements and compounds in water samples.
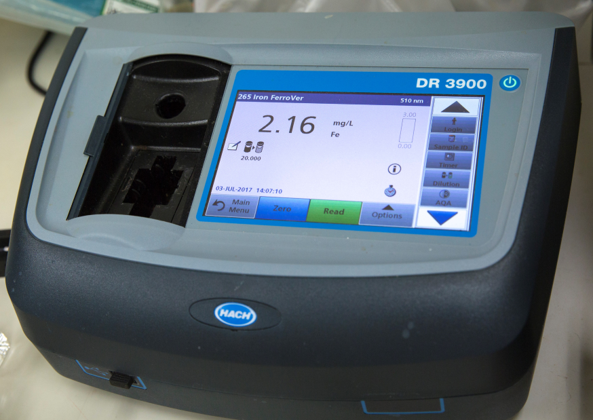
UV-Visible Spectrophotometer (Wavelength range: 190 - 1100 nm)
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometry is a technique used to measure light absorbance across the ultraviolet and visible ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. UV spectrophotometer use this principle to quantify the analytes in a sample based on their absorption characteristics. The device is used for the concentration measurements of several chemical elements and compounds in water samples.

Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP)
Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) is a technique that uses plasma source in which the energy is supplied by electric currents which are produced by electromagnetic induction, that is, by time-varying magnetic fields. ICP analysis is a powerful chemical analysis method which can be used to identify both trace amounts and major concentrations of nearly all elements within a water sample.

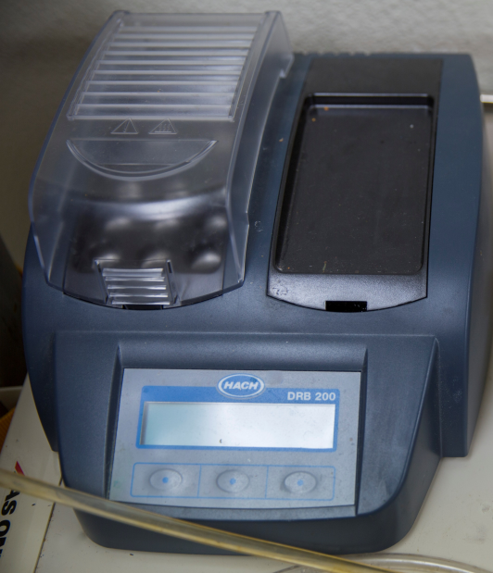
Digital Reactor Block (DRB)
Digital Reactor Block (DRB) is a dry thermostat reactor that provides unique one-key operation. The device is used for digestions for metals analysis, digestions for nutrients analysis, or culture biological samples by controlling temperatures in the reactor from 37 to 165°C in 1°C increments.

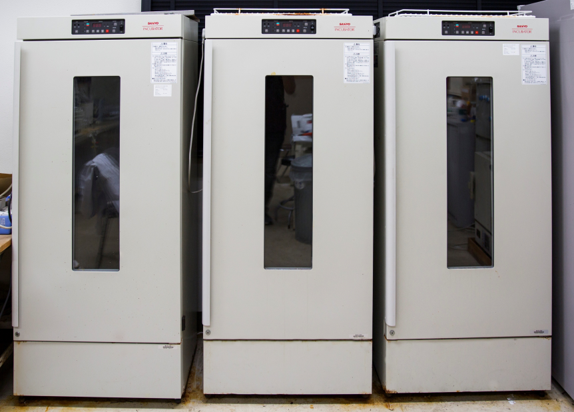
Incubator
Incubator is an insulated enclosure in which temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions can be regulated at levels optimal for growth, hatching, or reproduction. The device is used for conducting batch experiments that requires special temperature and environmental conditions and for the experiments that involve bacterial cultures.

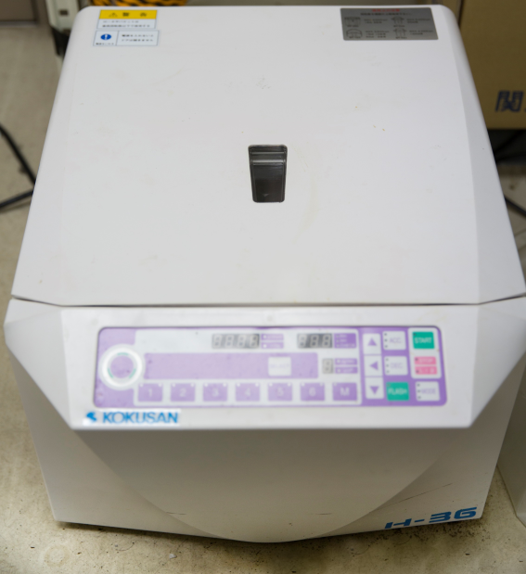
Lab Centrifuge
Centrifuge is a lab-device that facilitates harvesting and separating particulates in suspension. The device is used for rapid separation of precipitates from reaction mixtures or, at higher accelerations, for sedimentation of cell membrane fractions.




